Pharmaceutical packaging is more than just a box or container. It is a key component in the healthcare system. Its core missions are threefold:
- Ensure pharmaceutical safety
- Maintain pharmaceutical integrity
- Guarantee the stability of drug efficacy
From the moment drugs are produced to when they reach patients, packaging needs to prevent the following issues: Physical damage, Contamination, and Deterioration. It acts like a “silent guardian to protect public health and uphold people’s trust in brands
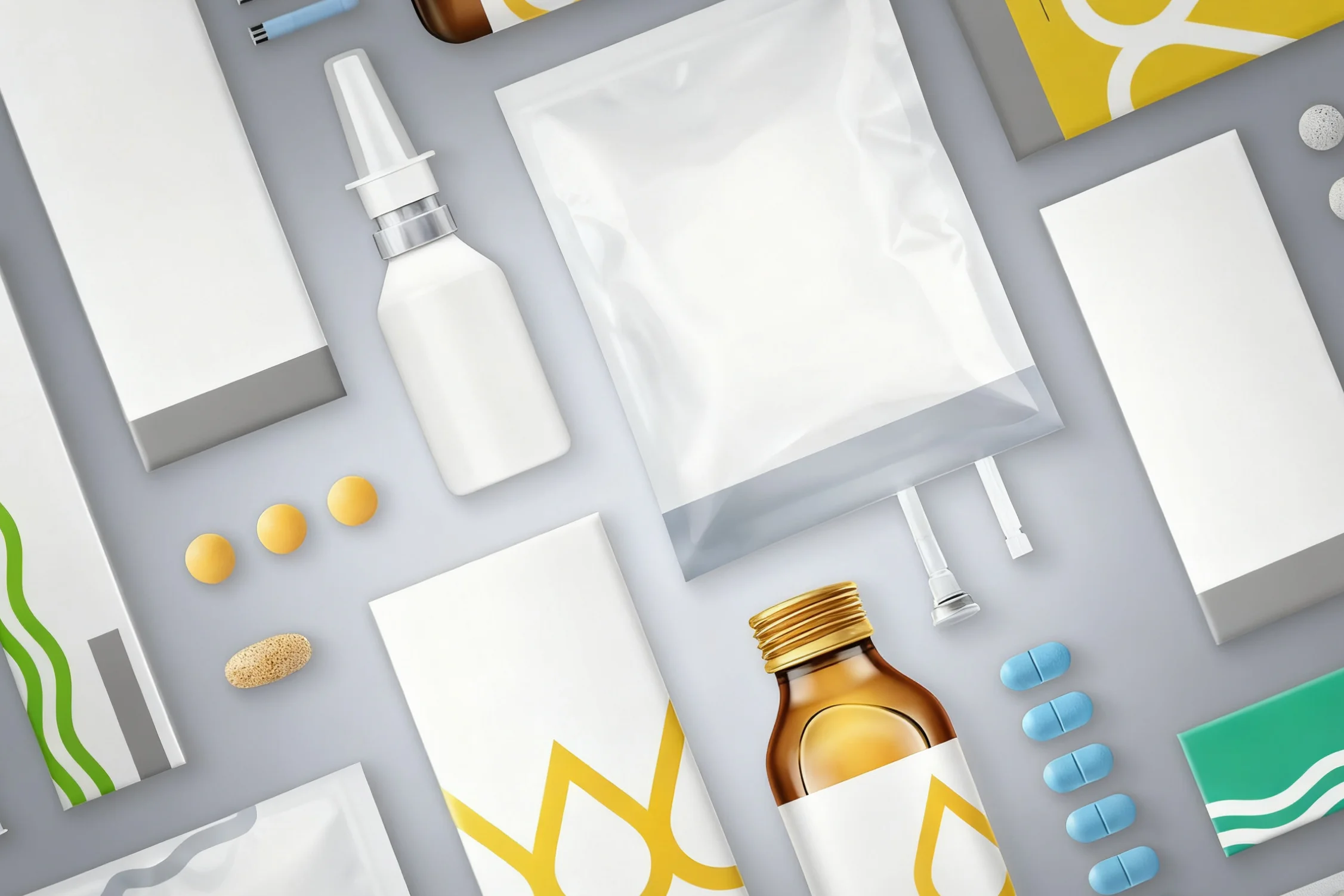

The Three-Layer Protection System
The pharmaceutical field is related to human lives. Product protection is a top priority. Leading companies all adopt a multi-layer protection strategy. Primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging. Each has a key role to play. Therefore, understanding this three-layer system is important. It is not just for logistics and transportation. It is more about ensuring drug efficacy and patient safety.
Primary Packaging: The Direct Guardian
Packaging that comes into direct contact with drugs.
Common types include:
- Blister packs
- Ointment tubes
- Vials
Main functions:
- Maintain drug stability
- Prevent drugs from reacting with environmental factors
What happens if drugs become unstable? Their efficacy will be completely lost. It needs to resist such environmental factors as moisture, light, and oxygen, so when we choose the right primary packaging, there are two factors to consider:
- the drug form (tablets, liquids, injectables)
- the drug sensitivity
Secondary Packaging: The Informative Shield
It refers to the medicine boxes you usually unpack. For example, the hard cardboard box outside the cold medicine has dosage instructions like “Take three times a day, one pill each time”. It has three main roles:
- Provide an extra layer of physical protection
- Facilitate brand display
- Carry key information
It provides additional physical protection, facilitates branding, and, most importantly, serves as the primary platform for critical information. Many medicine boxes have a tamper-proof design. You can tell if they have been opened. It makes people feel secure when using them.
Tertiary Packaging: The Logistics Protector
Designed for bulk handling and transportation.
Common types include:
- Shipping cases
- Pallets
As the outermost layer of packaging, its function is to ensure the safe transportation of drugs in the supply chain and guarantee transportation efficiency. During transportation, it needs to prevent problems like impact and collision, moisture, and dust. It protects until drugs reach their destination.
Material Science: The Foundation of Safety and Integrity
Choosing packaging materials is a science. Compatibility is key since drug formulations must match packaging containers so that we can ensure drugs remain stable throughout their shelf life.
Common packaging materials and their characteristics:
(1) Glass
- Excellent protective performance
- Stable chemical properties (not easy to react)
(2) Plastics
- Versatile uses
- High durability
- Flexible design
(3) Aluminium Foil
- Strong barrier property (moisture, oxygen, and light can hardly get in)
- Ensures long-term stability of sensitive solid-dose medications
Choose pharmaceutical packaging materials by three core factors: align with the drug’s chemical composition to avoid adverse interactions, match the required shelf life via material properties (e.g., barrier, stability), and strictly comply with regulatory standards.
IV. Beyond Protection: Compliance, Patient Safety, and the Smart Future
Modern pharmaceutical packaging is more than just for protection. It has become an intelligent platform to aid regulatory compliance, facilitating patient interaction and promoting sustainable innovation.
Among them, regulatory compliance is mandatory: it must meet the guidelines of institutions like the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), EMA (European Medicines Agency), and WHO (World Health Organization); packaging must conform to strict standards, including material standards, labeling standards, and quality control standards. Meeting these standards enables obtaining market access qualification and ensuring patient safety.
In addition, packaging also plays a key role in enhancing patient safety and medication adherence:
- Secondary packaging is crucial: labels must be clear and the design must be easy to understand, which helps prevent medication errors.
- Unit-dose blister packs have advantages: they simplify complex medication regimens and help patients take medicine on time and in the right dosage, thus improving adherence.
- Driving Sustainability and Innovation
Meanwhile, the pharmaceutical packaging industry is undergoing notable changes:
- Prioritizing environmental friendliness: using more eco-friendly materials, designing more eco-friendly packaging, and reducing environmental impact.
- Smart packaging on the rise: integrated with technologies such as NFC tags, QR codes, and temperature sensors, it can achieve functions including better drug tracking, enhanced patient interaction, and monitoring the status of drugs in the supply chain.

V. Conclusion
In conclusion, pharmaceutical packaging is no simple component—it is a strategically significant part of drug R&D and delivery, integrating material science, engineering, and regulatory knowledge as a multi-functional system. Its core goal of ensuring drug safety, effectiveness, and integrity benefits companies by aiding compliance, improving patient outcomes, building trust, and advancing sustainable healthcare. Practical solutions require partners with deep expertise and quality commitment, while principles like material science and compliance are daily practices for leading manufacturers, defining exceptional packaging.
VI. Why Choose Meishida as Your Pharmaceutical Packaging Partner?
As your trusted partner in pharmaceutical packaging, Meishida combines deep industry expertise with unwavering quality commitment to deliver tailored solutions that ensure product safety and supply chain integrity.
We have:
- 20+ years‘ experience in pharmaceutical packaging
- State-of-the-art facilities with controlled manufacturing environments
- End-to-end integrated production from printing to finished cartons
- Dedicated R&D for innovative and sustainable materials
- Certified quality systems (ISO22000, GMP, ISO9001)
- Full OEM/ODM support for domestic and international markets
Ready to transform your pharmaceutical packaging? Contact Meishida today for customized solutions that protect your products from primary materials to final delivery.






